AI detectors are useful but imperfect tools. They estimate the probability that text was generated by AI, but they don't deliver verdicts. Accuracy varies significantly depending on the tool, the text length, the writing style, and whether the content has been edited after generation. No detector currently achieves 100% accuracy, and any tool that claims otherwise is misleading you.
This guide breaks down how accurate AI detectors really are, what causes false positives and false negatives, how leading tools compare, and how to use detection results responsibly, whether you're a student, educator, or content professional.

What is Accuracy in AI Detection
Most people assume accuracy means one thing. In AI detection, it actually means three different things, and understanding the difference matters.
Accuracy is the overall rate of correct classifications: how often a detector correctly identifies text as either human-written or AI-generated across all samples.
Precision measures how often the detector is right when it flags something as AI. High precision means fewer false accusations. Low precision means the tool is trigger-happy flagging human writing it shouldn't.
Recall measures how much AI-generated content the detector successfully catches. High recall means fewer AI texts slip through. Low recall means the tool misses a lot.
In academic and professional settings, precision matters more than recall. Missing some AI-generated content is unfortunate. Wrongly accusing a student or writer of using AI when they didn't is far more damaging.
Here's why this distinction is critical: a detector can claim 99% accuracy on a curated benchmark while producing a 25% false positive rate on real student essays. Those two numbers can both be true, and knowing which one to trust makes all the difference.
How AI Content Detectors Actually Work
AI detectors use machine learning models trained on large datasets of both human-written and AI-generated text. When you submit content, the detector analyzes several layers of linguistic behavior simultaneously. The answer to these questions has already been explained in this guide on how AI content detectors work, but here’s a quick summary.
- Perplexity measures how predictable the text is. AI-generated content tends to be highly predictable, so the model always chooses the most probable next word. Human writing is more unpredictable, with unexpected word choices, stylistic detours, and occasional errors that raise the perplexity score.
- Burstiness measures variation in sentence length and structure. Human writing naturally mixes short, punchy sentences with longer, more complex ones. AI writing tends toward uniform sentence length and consistent structure — smooth and readable, but rhythmically monotonous.
- Entropy is closely related to perplexity and measures the overall unpredictability of the text. Low entropy across a long passage is a strong signal of AI involvement.
- Structural and semantic analysis looks at paragraph symmetry, argument balance, transition patterns, and semantic consistency. AI essays tend to explain every point with similar depth and structure. Human writing lingers on some ideas and rushes through others.
Detectors compare your text against these learned distributions and return a probability score, not a binary label. Reputable tools express this as a confidence range. Binary AI or Human labels without context encourage misuse and create a false sense of certainty.
How Accurate Are Leading AI Detectors: Based on Tests
Accuracy claims vary widely across tools, and the methodology behind those claims matters as much as the numbers themselves.
I used 100 samples: 50 written by students and 50 by ChatGPT. Each piece was run through all five detectors to track false positives (human flagged as AI) and false negatives (AI flagged as human).
Which AI detector is the most accurate? Here's how the major tools compare based on available data and independent testing:
| Tool | False Positives (Human flagged as AI) | False Negatives (AI flagged as Human) | Overall Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| JustDone AI Detector | 8% | 12% | 90% |
| GPTZero | 20% | 10% | 85% |
| Turnitin AI Detection | 28% | 8% | 82% |
| Copyleaks | 18% | 15% | 83% |
| Originality.ai | 25% | 10% | 82.5% |
One important finding from independent testing: a 2025 study found that while many detectors claim accuracy above 99% on curated benchmarks, performance drops dramatically in the wild when analyzing real student essays or lightly edited content.
JustDone's AI Detector performed best in independent comparative testing for false positive balance. For instance, let's check it on the First chapter of “Wuthering Heights” by Emily Brontë.
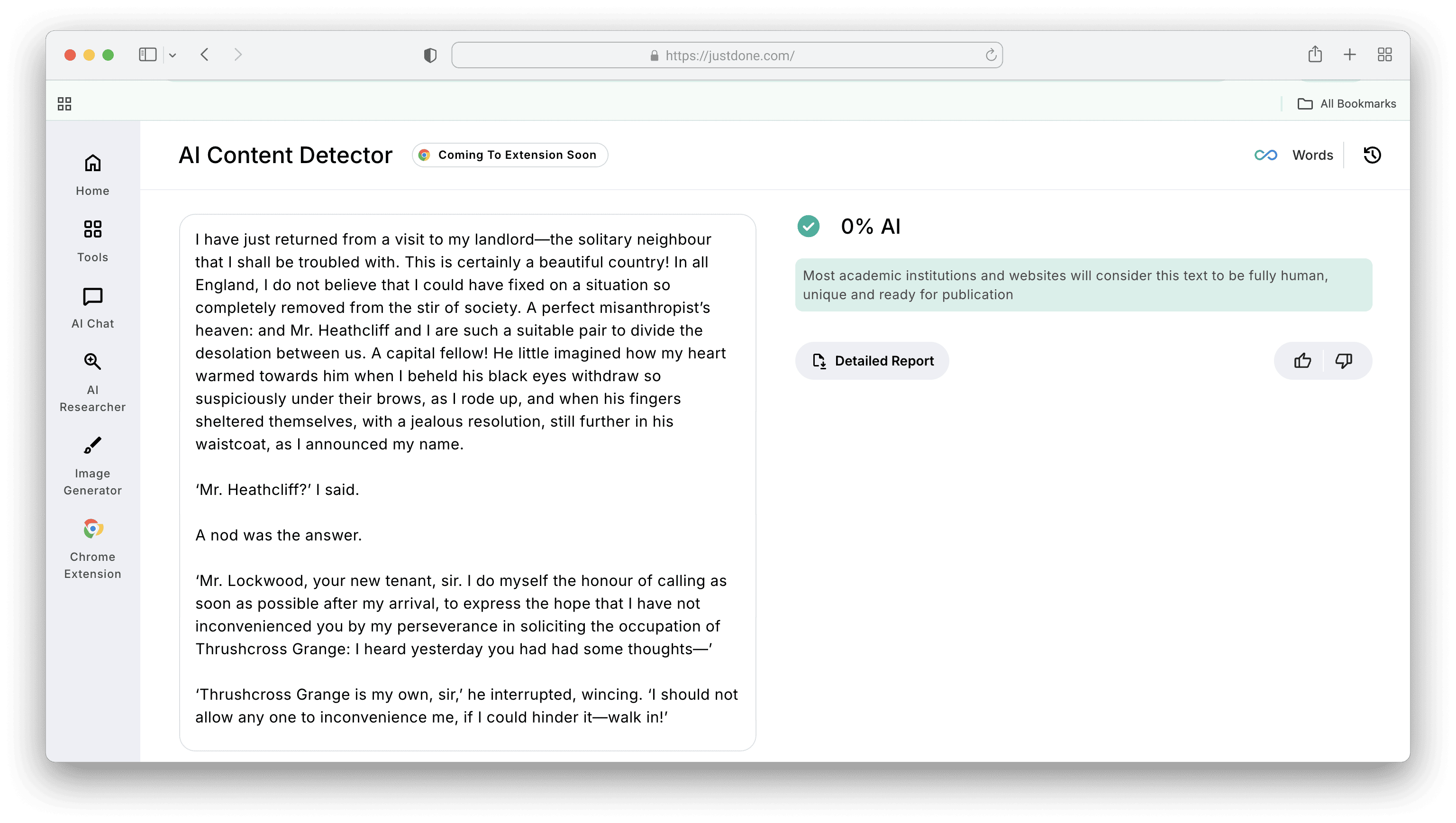 The tool correctly identifying human-written literary analysis that multiple competitors flagged as AI, while still catching lightly edited AI-generated content that others missed.
The tool correctly identifying human-written literary analysis that multiple competitors flagged as AI, while still catching lightly edited AI-generated content that others missed.
The False Positive Problem
A false positive occurs when a detector flags human-written content as AI-generated. This is the most consequential error AI detectors make. It happens more often than most people realize.
Real consequences include academic misconduct investigations, loss of scholarships, rejected articles, damaged professional credibility, and significant emotional harm.
A University of North Georgia student named Marley Stevens was placed on six months of academic probation and lost her scholarship after her essay was flagged. She had only used Grammarly for grammar checks.
Why does it happen?
Several types of legitimate human writing trigger false positives:
- Formal academic writing — structured essays with clear thesis statements, balanced paragraphs, and logical transitions closely resemble AI output to a detector analyzing patterns rather than meaning.
- Experienced, polished writers — consistent fluency and disciplined prose can mirror AI patterns, even when the work is entirely original.
Instructional and procedural content — step-by-step explanations and structured guides follow predictable patterns that detectors associate with machine output. - Technical writing — precision and clarity in technical documentation can look too clean to a detector expecting more variation.
The lesson: a high AI score is a signal worth investigating, never a standalone verdict.
Who Is Most at Risk from Inaccurate Detection?
There are three main groups of writers who are flagged (often wrongly) with AI texts:
- Non-native English speakers
This is the most serious documented bias in AI detection. A Stanford study found that 20% of essays by non-native English speakers were wrongly flagged as AI-generated, compared to significantly lower rates for native speakers. Non-native writers tend to use simpler sentence structures, prioritize clarity over stylistic complexity, and avoid idiomatic language. These characteristics overlap significantly with AI writing patterns, making ESL students disproportionately vulnerable to false accusations. - Students writing in formal registers
Academic writing conventions, such as thesis statements, topic sentences, structured arguments, formal transitions, are exactly the patterns detectors associate with AI. A student writing well, by the book, is more likely to be flagged than one writing conversationally. - Writers working in specialized domains
Technical writing, legal writing, and scientific prose all tend toward low burstiness and high predictability. Detectors trained on general-purpose text may struggle with domain-specific writing styles.
AI Detection Limitations
Even the best detectors have real constraints that users need to understand.
Edited AI content is harder to detect. When AI-generated text is substantially revised by a human — restructured, paraphrased, expanded — detection accuracy drops sharply. A 2024 study showed performance falling by more than half when AI texts were lightly edited.
Short texts are unreliable. Detectors need enough linguistic data to identify patterns. Passages under 150–200 words produce much less reliable results.
Language bias. Most detectors are trained primarily on English-language data. Performance on other languages varies significantly and is often not disclosed by tool providers.
AI is evolving faster than detection. Modern models like GPT-5, Gemini, and Claude produce increasingly human-like text, including emotional tone, nuanced argumentation, and personal reflection.
No detector can determine intent. A tool can estimate whether text resembles AI output. It cannot tell you whether the writer used AI ethically, irresponsibly, or not at all.
How to Use AI Detectors Responsibly
Here are my recommendations on how to use AI checkers the right way:
- Treat scores as indicators, not verdicts. A high AI score means the text shares characteristics with AI writing. It does not prove AI was used. Always pair detection results with human judgment and context.
- Run a self-check before submission. Use JustDone's AI Detector to see which sentences are flagged before your professor or editor does. The sentence-level highlighting shows exactly where to focus your revisions — so you're editing with direction, not rewriting blindly.
- Build a writing audit trail. Keep your drafts, notes, and version history. If your work is flagged, a clear revision history is far more persuasive than any argument about the score. One student avoided a misconduct investigation by producing a screenshot of her handwritten outline and her Google Docs version history showing how her essay evolved.
- Understand your institution's policy. Acceptable AI use varies widely between institutions, courses, and assignment types. Don't assume — check your syllabus or ask directly.
For educators: use detection as a conversation starter, not a conviction. The most responsible use of AI detection in academic settings is to identify content that warrants a closer look and a conversation.
Final Verdict: Should I Trust Al Detectors?
AI detectors are improving, but they’re still fallible. Students deserve fair, accurate tools that support learning, not punish honest work. Are Al detectors reliable? When asking how accurate AI detectors are, remember that the answer depends on the tool and the context.
Out of all the ones we tested, JustDone's AI Detector offers the most balanced approach. It keeps false positives low while still catching AI-generated text effectively.
In the end, AI detectors should empower both students and teachers to engage in honest, thoughtful learning. Use them wisely and never forget the human side of writing.