A recent survey shows that about 39% of students use LLMs to answer assessments and nearly 7% use them to write entire papers. I've seen firsthand how universities are changing the way they manage academic integrity. The rise of AI-generated writing tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and others has opened new opportunities for learning, but it's also made it harder for educators to assess the authenticity of student submissions. That’s why more and more institutions are turning to AI detectors to maintain fair and ethical academic standards. But what AI detector do colleges use?
This is a question I frequently receive from students who are genuinely trying to understand the new academic landscape. If you're submitting work you wrote independently but used AI tools to help you brainstorm or organize, you may worry about being flagged unfairly. And honestly, I don't blame you. The tech isn't perfect, and in some cases, it can misinterpret genuinely human work or well-edited drafts as AI-generated content. So let’s walk through how colleges use these tools, what the most popular detectors are, and what you, as a learner, need to know.
Do Colleges Use AI Detectors in Practice
AI detectors are primarily used by universities to uphold academic honesty policies. In the 2025 survey, in which 1,681 faculty members at 52 higher institutions from 28 countries participated, 83% of them expressed concern over students' ability to evaluate critically AI-generated texts. Only 17% felt they reached an advanced or expert level of AI literacy. This means many professors are worried; some use tools, but many don't feel confident yet.
For students, it means that if an instructor suspects that a student may have used generative AI to complete an assignment, they might run the submission through one of these detectors. In some schools, essays are automatically scanned through an integrated detection tool upon submission, especially if they go through platforms like Turnitin or Canvas.

From my time as a student, I noticed that detection tools were often reserved for final papers, theses, and high-weight assignments. Some instructors would openly inform students that they were using AI detection software, while others preferred to run scans discreetly, only bringing up results if something seemed off. The ambiguity can create anxiety, especially since students rarely get to see the AI detection reports themselves.
Instructors don’t use these tools as the sole basis for penalizing a student. They usually look at them as one piece of evidence. If a detector flags a piece of writing as likely AI-generated, a discussion usually follows. That said, there’s still a lot of inconsistency between institutions and even departments within the same school.
Top 4 AI Detectors Most Commonly Used by Colleges
Now, to the heart of the question: what AI detector do colleges use? Based on what I’ve seen across institutions, here are five detectors that are most commonly used in academic settings.
- Turnitin
Turnitin's AI Writing Detection feature is by far the most widely used tool. Turnitin is already integrated into many LMS platforms, and with the rise of AI writing tools, they added their own detection model in 2023. Its interface shows educators the percentage of content believed to be AI-generated. Turnitin claims high accuracy, but many users, myself included, have experienced false positives. Still, its adoption rate in higher education is unmatched due to its longstanding presence in plagiarism detection. - GPTZero
GPTZero is another popular tool among individual educators and smaller institutions. It’s accessible and straightforward, with an easy-to-read report that highlights text likely to be AI-written. What makes GPTZero useful is its simplicity, but it's less commonly integrated into course management systems. I’ve seen professors use it as a secondary check when Turnitin flags something. - Copyleaks
Copyleaks has gained attention for offering both plagiarism and AI detection. It can be integrated into various educational platforms and offers a nuanced breakdown of AI vs. human-generated content. Some universities that value detailed detection reports use Copyleaks because of its robust analytics, especially for multilingual content. - Originality.ai
Originality.ai is often used more in publishing and corporate settings, but some colleges are exploring it for academic use, especially in departments that emphasize writing-intensive projects. What stands out about Originality.ai is its real-time scanning and ability to work with large volumes of data.
What Learners Need to Know About AI Detection in College
Let's look at the study that evaluated AI detection tools applied to more than 1,000 academic texts (750 AI-generated and 250 human). AI detectors showed moderate to high success in detecting whether the texts were AI or human. However, none of them reached perfect reliability. Human texts had lower false positive and AI-generated rates.
That means rewriting in your own words, adjusting tone and logic, and most importantly, understanding what you’re submitting. JustDone’s AI detector can help you check your work beforehand to avoid surprises. One of the things I like about it is that it doesn’t just give you a score; it gives you actionable insights to revise.
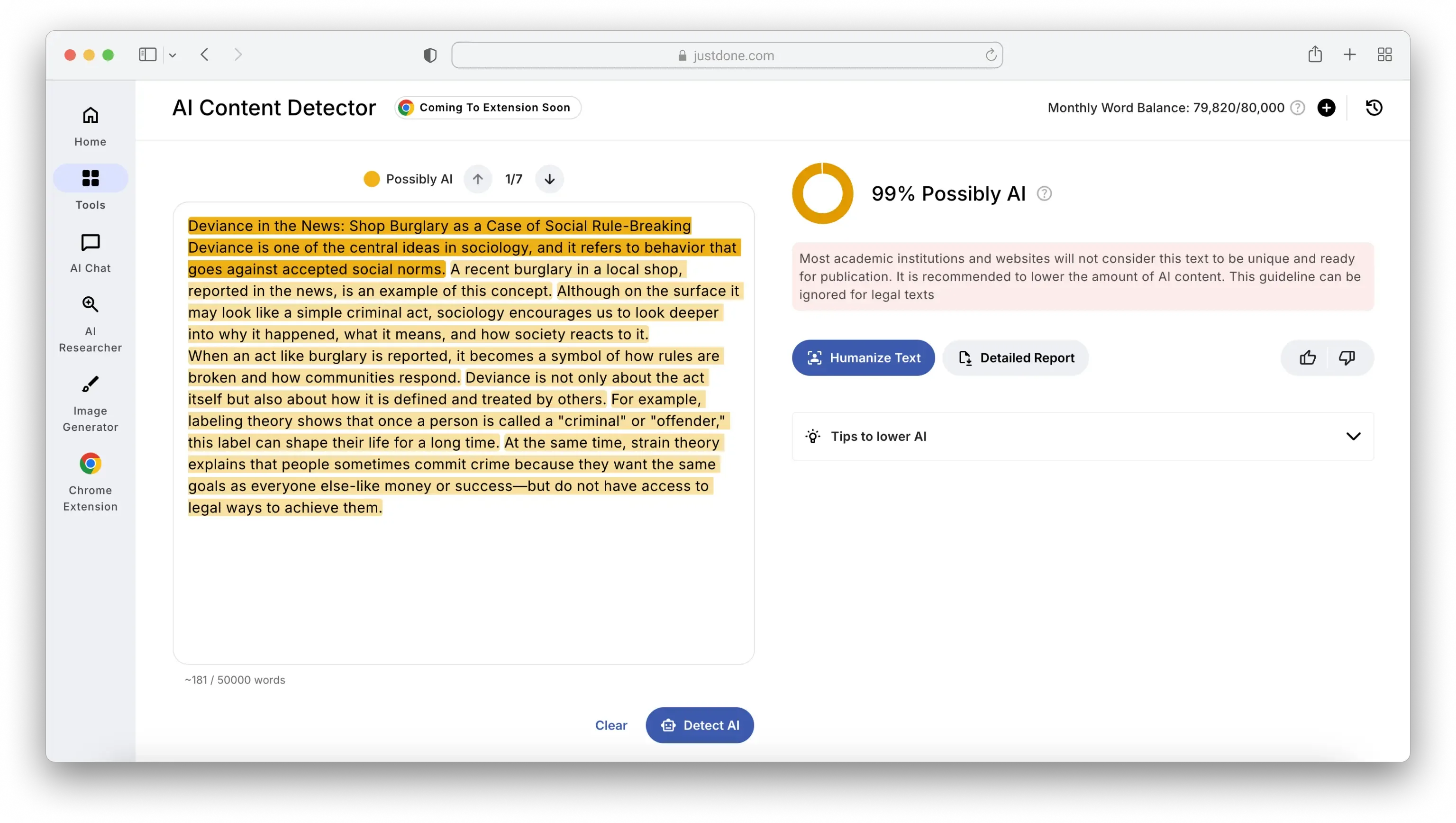 The biggest misconception I hear from students is that using AI tools automatically equals cheating. That’s not always the case. In many classes, using AI for idea generation, outlining, or grammar improvement is completely acceptable as long as you're transparent about it and not submitting AI-written text as your own.
The biggest misconception I hear from students is that using AI tools automatically equals cheating. That’s not always the case. In many classes, using AI for idea generation, outlining, or grammar improvement is completely acceptable as long as you're transparent about it and not submitting AI-written text as your own.
However, the line gets blurry when you start editing large chunks of AI-generated text. Most detectors flag this kind of hybrid writing because the patterns (structure, predictability, and vocabulary) can differ from natural human writing. I had one student approach me last semester in tears because their rough draft, edited with ChatGPT for grammar, was flagged by Turnitin. Luckily, their professor reviewed the full history in Google Docs and saw that the work evolved from their original idea. That level of transparency saved them.
No AI detector is 100% accurate. Most are trained on datasets from tools like GPT-3 or GPT-4, which means they struggle with more subtle uses of AI, human-edited content, or multilingual texts. This is why it’s risky to rely too heavily on any single detection tool.
From an academic strategy perspective, you should aim for transparency and authenticity. If your college allows AI tools as long as you acknowledge them, take that opportunity. In fact, some instructors now ask students to include a short statement on how AI tools were used, much like declaring help from a tutor or editor. This shows integrity and keeps you safe if a detection report ever comes up.
The Bigger Picture: Evolving Standards in Higher Education
We’re still in the early days of understanding how AI will shape education. Institutions are trying to figure it out just like students are. While AI detectors are helpful for maintaining academic standards, they’re also shaping new conversations about what it means to write and learn in an AI-supported world.
Some colleges have even started offering workshops to teach students how to use AI ethically, focusing on learning enhancement rather than punishment. That shift gives me hope because it acknowledges that AI isn’t going away and banning it entirely isn’t realistic. Instead, the goal is to teach students how to collaborate with AI tools responsibly.
Final Thoughts on AI Detectors That Colleges Use
If you're wondering what AI checkers colleges use, you’re really asking a bigger question about academic values in the age of intelligent machines. Turnitin leads the pack, but others like GPTZero, Copyleaks, Originality.ai, and Crossplag are gaining ground. Students should understand not only how these tools work, but also how to navigate them ethically and effectively. And if you’re ever in doubt, run your content through JustDone’s AI detector. It might just be the extra layer of assurance you need before hitting submit.