Key takeaways:
- Plagiarism is not AI detection. Plagiarism tools find matches to sources; AI detectors flag machine-like writing patterns.
- AI isn’t automatically plagiarism. It becomes misconduct when you submit work that isn’t meaningfully yours or you break policy/disclosure rules.
- Fast workflow: check plagiarism first – fix matches/citations – run AI check – rewrite only flagged parts with more specificity plus your own interpretation.
No matter how solid your academic paper is, there is always a doubt like “What if this gets flagged?” Usually, students mean one of two things: plagiarism (text matches existing sources) or AI detection (the writing looks machine-generated). The problem is that these are different risks, measured in different ways, and one tool rarely replaces the other.
In this guide, you’ll learn the difference between plagiarism checkers and AI detectors, whether plagiarism tools can detect AI (usually no), when AI use can become plagiarism, and a practical workflow to check your draft without spiraling.
Plagiarism checkers vs AI detectors: What Each Tool Measures
Here’s a short breakdown of what both tools do and how they are helpful for learners.
What a plagiarism checker does
A plagiarism checker compares your text against a database (web pages, publications, student papers, depending on the tool). It highlights matching passages and returns a similarity score. This is why plagiarism reports often show exact sources and exact matched lines.
Plagiarism tools are good at catching:
- copied paragraphs
- patchwork paraphrasing that stays too close to the original
- missing quotation marks or missing citations
- reused template text
What an AI detector does
AI detectors don’t primarily search for source matches. They look for patterns that resemble machine writing – things like unusually uniform sentence structure, overly smooth phrasing, low “burstiness,” or generic transitions.
Tools in this category try to answer: “Does this read like it was generated?” (Not: “Was this copied?”)
A useful real-world reminder: Turnitin reported that after reviewing a very large volume of student writing, 11% of papers were flagged as potentially having AI-written content in at least 20% of the document, and 3% were flagged as having 80% or more AI writing. They also stated a false positive rate of <1% when analyzing full documents.
Key takeaway: plagiarism checks matching content. AI detection checks writing patterns.
Is it plagiarism to use AI
In fact, to understand if this is plagiarism when you use AI depends on how you use it.
AI use becomes plagiarism (or academic misconduct) when you submit work that isn’t meaningfully yours and present it as your own, especially if it includes unattributed borrowed ideas, wording, or structure, or violates your institution’s policy.
AI use is less likely to be considered plagiarism when you use it like a learning assistant (for brainstorming, outlining, editing, clarity improvements), and you still do the reasoning, verification, and final writing choices. Plus, discloses AI usage if your course requires it.
In other words: AI is a tool. The academic risk comes from misrepresentation and lack of attribution/policy compliance, not from the mere fact that AI touched your text.
Top AI and Plagiarism Detection Tools Tested
In academic writing, it’s common to see more than one detection method used at the same time. Some tools focus on plagiarism by scanning text against published sources and scholarly databases. Others look for AI-writing patterns based on language signals like sentence structure, predictability, and style consistency. In many universities, instructors rely on platforms that combine these checks, which is why students often feel like they need a “full” review before submitting.
Some platforms include both plagiarism checking and AI detection, which makes them popular in academic environments:
- Turnitin often includes plagiarism checking and an AI writing indicator (depending on the institution’s setup).
- Copyleaks provides plagiarism checking and AI detection as separate products within one ecosystem.
- Originality.ai is marketed as an AI + plagiarism detector and is more common in SEO/publishing, but students still run into it when searching for “AI and plagiarism checker” tools.
Many students use a separate-but-simple setup:
- Plagiarism check using Turnitin (if available) or another standalone checker
- AI pattern check using an AI detector like GPTZero-style tools
This workflow still works well—, specially when you want a second opinion and don’t depend on just one score.
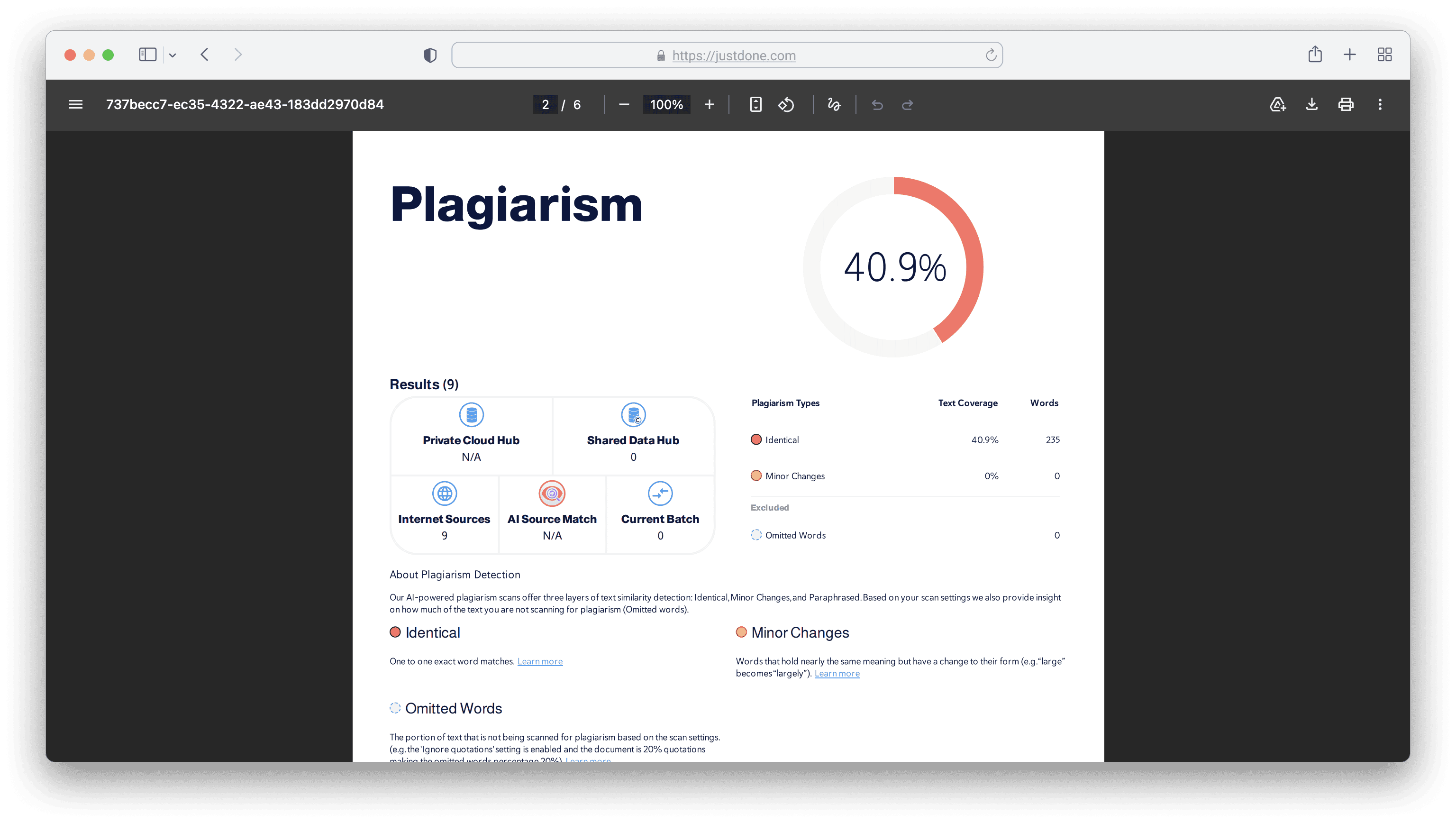
Here's what I recommend instead and have already tested. One of my favourites is JustDone Plagiarism checker. So, I selected a journal article about Shakespeare's play on writing a dissertation and extracted a few paragraphs.
Then, I plugged this into JustDone’s plagiarism checker. It flagged it as more than 40% matched with the different web sources. The detailed report looks like this:
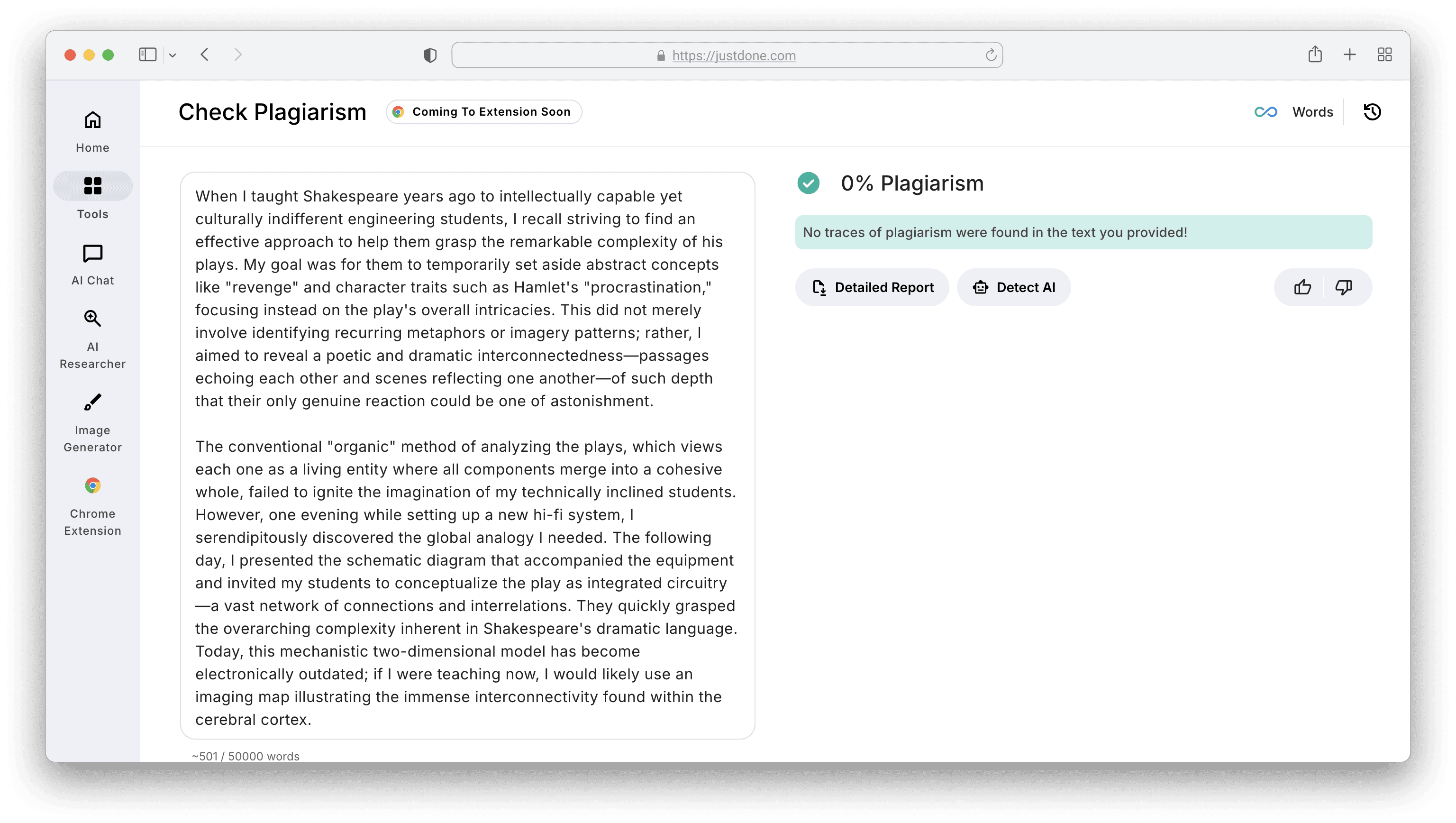
 The tool allows a Remove Plagiarism option, so I decided to test this option. JustDone plagiarism checker paraphrased the text, so I got 0% similarity score as a result.
The tool allows a Remove Plagiarism option, so I decided to test this option. JustDone plagiarism checker paraphrased the text, so I got 0% similarity score as a result.
Then, I scanned the revised text through JustDone AI detector. It flagged the overly academic tone and a bit of stiff language.
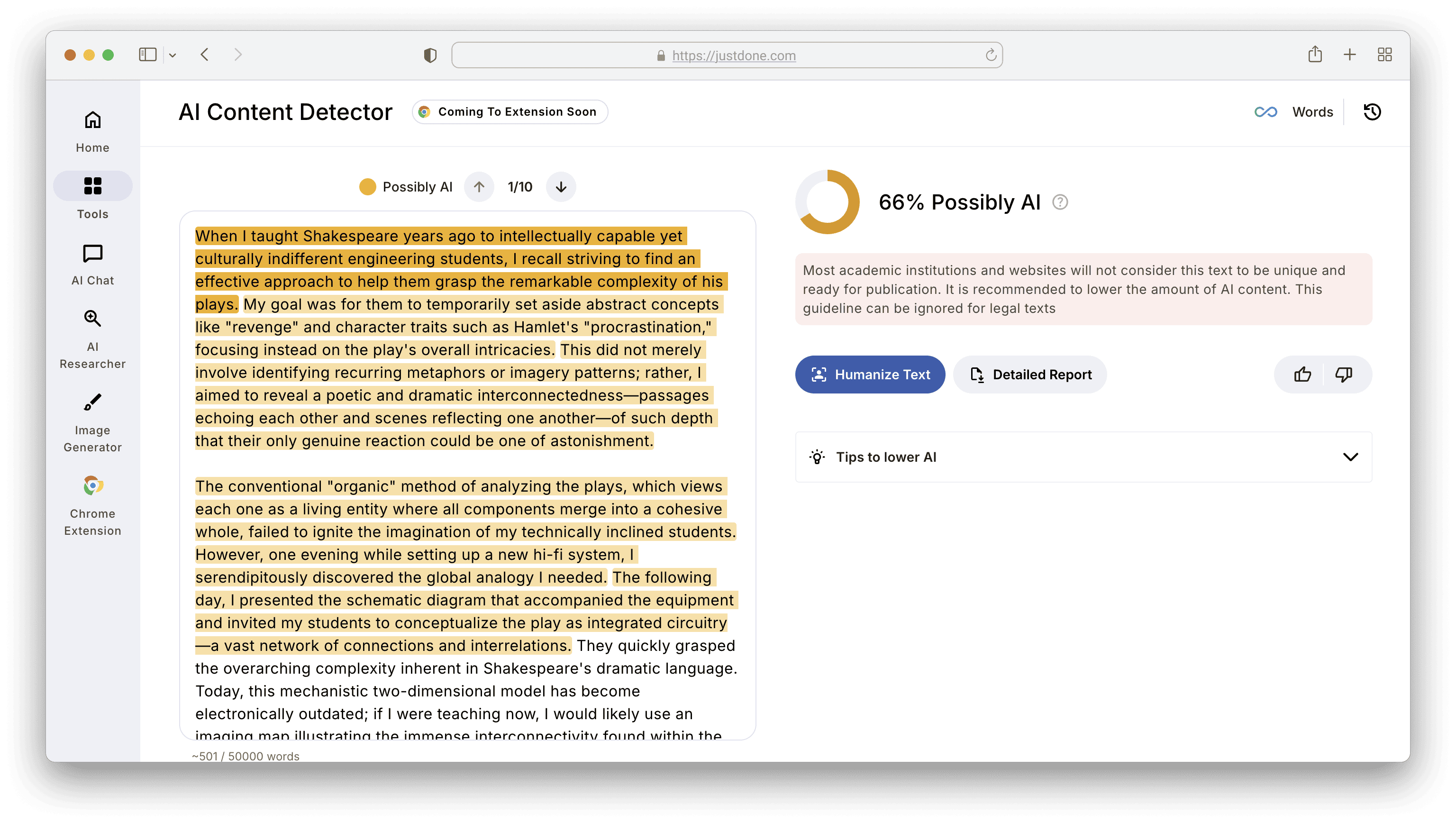
AI detection rate is not the verdict, but 66% is a lot. So, I used AI humanizer to make the text less formal and more personal to lower the score. The result was good. Just needed a manual check of the text's structure, add personal examples, and double-check citations.
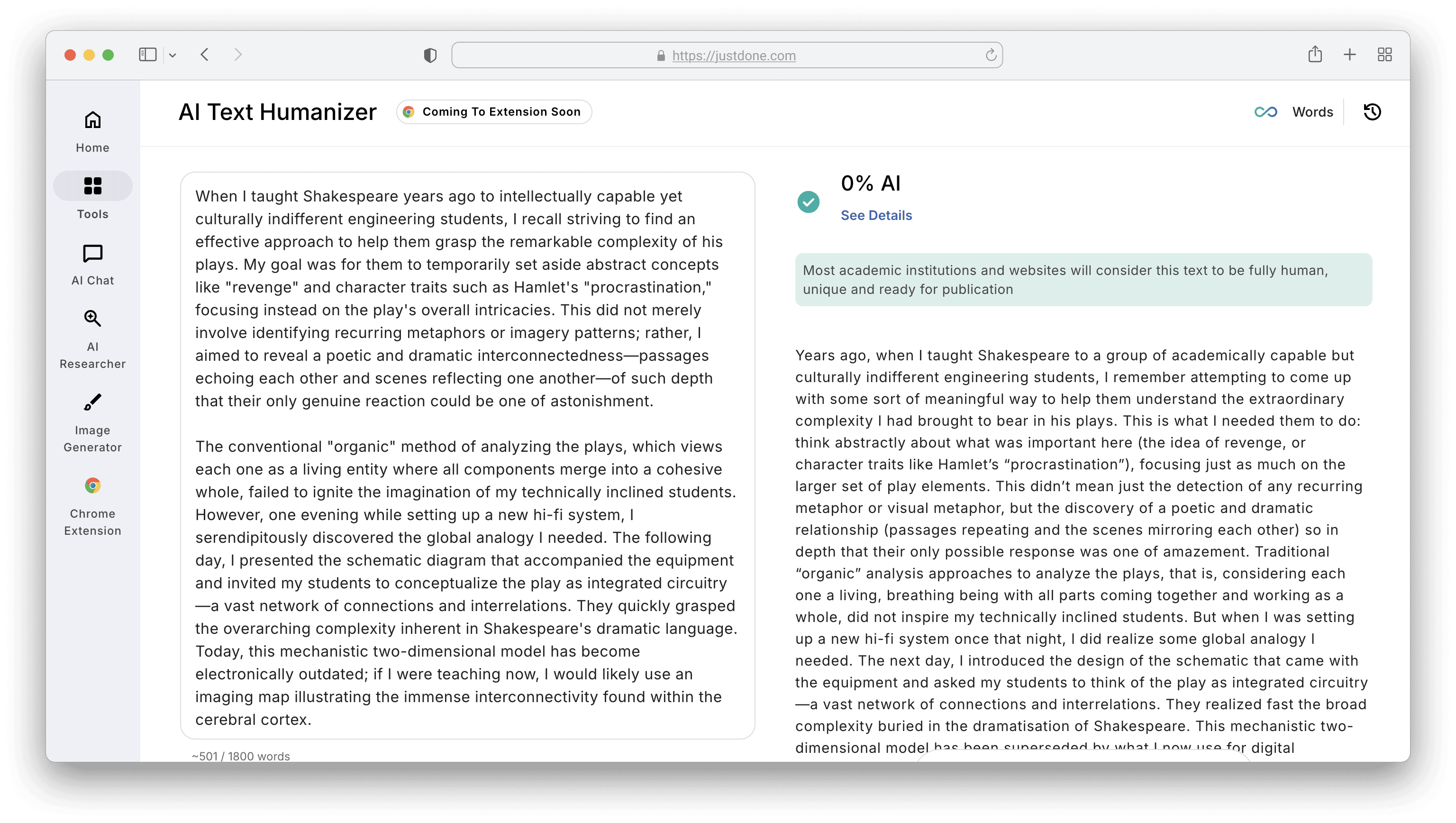
The main problem isn’t just choosing tools, but it’s the stress of switching between them. That’s why platforms like JustDone fit naturally into student workflows: they combine plagiarism checking and AI detection in one place, so you can review originality and AI patterns without bouncing across multiple tabs right before submission.
Do plagiarism checkers detect AI
Most of the time, no. Plagiarism tools can only flag AI-written text if that AI text contains phrasing that already exists somewhere in the databases they scan.
That’s why students get confused: an AI-written paragraph can be “original” (not copied from any source) and still be flagged as AI-like. And a human-written paragraph can be flagged for plagiarism if it matches a source too closely, even if the student didn’t “intend” to copy.
What Students Ask About These Tools
Here are the 5 most often asked questions students should know about plagiarism checkers and AI detectors:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Do plagiarism checkers detect AI? | No, they match text to sources, not writing style. |
| Can AI be detected for plagiarism? | Only if AI copied existing text; original AI text won’t register. |
| Free plagiarism checker + AI tool? | Yes, tools like JustDone, GPTZero, Copyleaks offer free tiers. |
| Which is better for essays? | Both: plagiarism to check citation, AI detection to ensure original tone. |
| What score is "too AI"? | Not more than 15% if use AI checker. No fixed percent by plagiarism checkers, but aim for low AI detection and human tone overall. |
Best Workflow for Students
Here’s the cleanest process I recommend (and it’s fast once it becomes habit):
Start with plagiarism first. If your similarity report highlights large matching blocks, fix those before you even think about AI detection. Most AI anxiety is wasted time if your citations/paraphrases aren’t clean yet.
Then run AI detection on the revised draft. If something is flagged:
- don’t rewrite the whole paper
- rewrite only the flagged sections by adding specificity, varying sentence rhythm, and inserting your own interpretation after citations
Finally, do a last pass for human markers that are normal in real student writing: a clear stance, a concrete example, and a sentence that explains why a source matters for your argument (not just what it says).
How to Spot False Positives in AI and Plagiarism Checks
Both types of tools can make mistakes. As this research shows, false positive results are the trickiest and especially affect non-native English speakers. That means a student who writes more creatively or with less standard structure is more likely to be flagged, even if they don't use AI.
Academic phrases like “In conclusion” or “The study indicates” may trigger plagiarism alerts, even if legitimately cited. Some AI detectors can be overly cautious about formal writing.
When your text gets flagged, don’t panic. These tools are guides, not judges. If a detector flags something as AI-generated, ask: Does it sound robotic? Are all your sentences the same length? If so, rewrite for variety and personality. If the plagiarism checker highlights a phrase you cited properly, double-check that the quote is in quotation marks or properly paraphrased, and move on.
Final Thoughts on Plagiarism and AI Detectors
Plagiarism and AI checkers serve different purposes: one tests what you wrote (source originality), the other tests how you wrote it (human touch). As a student, using both, followed by human review, is your best path to integrity and authenticity. Tools like JustDone offer both services under one platform, and their free tier is a great start. But none can replace your judgment. Always aim for clarity, personal voice, and proper citations. Ultimately, tech can guide you, but your thinking is the real star of the show.